IgG4-related disease clinical profiles
Last updated May 20, 2025, by Lindsey Shapiro, PhD

Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD), a systemic, or body-wide, disease marked by inflammation and scarring (fibrosis), can affect nearly every organ in the body and manifest in many different ways.
In most cases, the disease involves several organs at the same time, and displays a dominant clinical profile of the four typical profiles identified to date. While all four clinical profiles arise from the same underlying disease process, their signs and symptoms differ based on which specific organs are most impacted.
How IgG4-RD is classified
IgG4-RD has only been recognized as a distinct disease since the early 2000s, when a group of separate fibroinflammatory conditions involving various organs were unified under the umbrella term IgG4-RD. Now, those conditions are recognized simply as different organ manifestations of a single IgG4-RD disease process.
While scientists don’t fully understand the IgG4-RD causes, in all cases, immune cells, especially plasma cells that secrete IgG4 antibodies, infiltrate tissues and cause inflammation and fibrosis. These processes, along with the resulting tumor-like masses and swelling, can damage organs or interfere with their normal function.
Because the condition can manifest in many different ways over time in the same person, there are no well-defined types of IgG4-RD. However, there are patterns of organ involvement that tend to appear more commonly.
Such IgG4-RD classification can help doctors reach an IgG4-RD diagnosis, predict what IgG4-RD symptoms or complications are most likely, and decide which interventions are needed.
Main clinical profiles of IgG4-RD
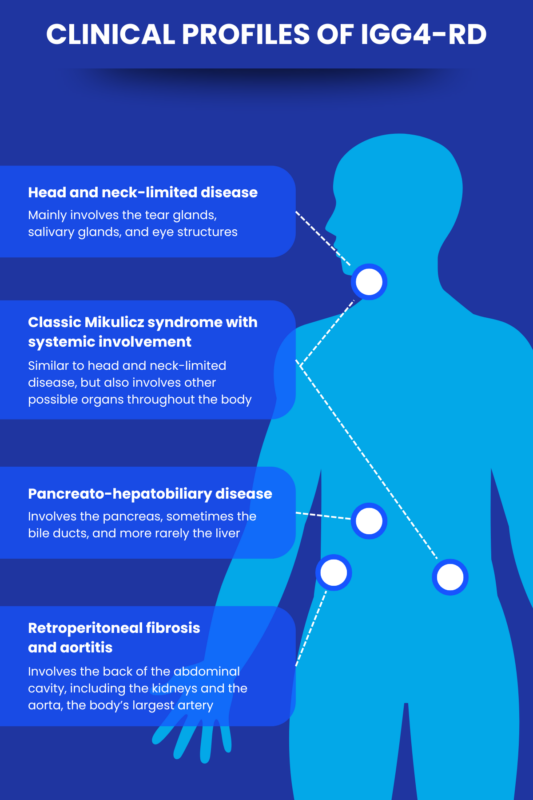
A 2019 study described four clinical profiles that are seen most commonly in IgG4-RD patients: pancreato-hepatobiliary disease, retroperitoneal fibrosis and/or aortitis, head and neck-limited disease, and classic Mikulicz syndrome with systemic involvement.
Pancreato-hepatobiliary disease
This profile is generally characterized by involvement of the pancreas, with or without involvement of bile ducts, which carry the digestive fluid bile out of the liver. Less often, the liver could be directly impacted.
Pancreato-hepatobiliary disease may typically cause:
- type 1 autoimmune pancreatitis, characterized by pancreas inflammation
- sclerosing cholangitis, where the bile ducts become inflamed and scarred.
- jaundice, a yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes
- abdominal pain
- gastrointestinal issues
- diabetes.
This clinical profile is more common in men than in women, similar to the overall trend in IgG4-RD.
Retroperitoneal fibrosis and aortitis
Here, the retroperitoneum — the area in the back of the abdomen where several tissues and organs are located, including the kidneys and the aorta — is the mainly affected part of the body. The aorta is the body’s largest artery that runs from the heart down through the abdomen.
This clinical profile, also showing a male predominance, mainly manifests as:
- retroperitoneal fibrosis, or scarring in the retroperitoneum, a condition previously known as Ormond’s disease
- aortitis, or inflammation of the aorta.
Symptoms may include:
- side or back pain
- leg swelling or pain
- urinary changes and other signs of kidney disease.
Head and neck-limited disease
In this clinical profile, disease manifestations mainly occur in areas around the head and neck, including the tear (lacrimal) glands, salivary glands, and tissues surrounding the eyes.
This profile, which has been reported more commonly in women, encompasses conditions previously known as:
- Mikulicz’s disease, marked by persistent swelling of the lacrimal and salivary glands
- Küttner’s tumor, a swelling of the salivary glands.
Head and neck-limited disease can lead to several symptoms, including:
- painless swelling in the face or neck
- eye issues, including bulging eyes, pain during eye movements
- mild dry eyes or mouth.
Classic Mikulicz syndrome with systemic involvement
This classification looks like what was previously known as classic Mikulicz syndrome. Like with head and neck-limited disease, the lacrimal and salivary glands are affected, but there’s also involvement of other tissues and organs.
As such, people with this profile, which affects more men than women, may experience a wide range of symptoms.
Other organ manifestations
IgG4-RD can also affect a range of other organs and cause a variety of symptoms, including:
- Riedel’s thyroiditis, a type of thyroid disease
- lymphadenopathy, the enlargement of lymph nodes
- pulmonary disease
- hypophysitis, inflammation of the pituitary gland in the brain
- pachymeningitis, involvement of the outermost membrane covering the brain.
How IgG4-RD clinical profiles influence disease severity
Any of these manifestations of IgG4-RD can become severe if the disease is not diagnosed and treated promptly. In general, some factors that could influence disease severity and IgG4-RD life expectancy include:
- involvement of vital organs
- involvement of multiple tissues and organs versus a single one
- a greater degree of tissue fibrosis, which can impair organ function.
But it is important to understand that even if a person doesn’t currently have involvement in any vital organs, like in the case of head and neck-limited disease, that does not mean such organs won’t eventually be impacted.
As such, for any form of the disease, delays in diagnosis can increase the risk of more severe symptoms and worse outcomes. It’s important to let a doctor know as soon as any possible signs of IgG4-RD are noticed.
How IgG4-RD clinical profiles influence treatment
Regardless of which organs are affected, IgG4-RD treatment is usually the same, involving corticosteroids or other immunosuppressive medications to keep inflammatory disease activity under control.
But in some cases, surgical interventions are needed when these medications aren’t sufficient, or if immediate intervention is needed before those treatments kick in. This will depend on the specific organ that’s involved and exactly how the disease is manifesting. Examples include:
- surgery to restore bile flow for those with pancreato-hepatobiliary disease
- surgical procedures to restore urine flow from the kidneys for those with retroperitoneal fibrosis
- surgical removal of tumor-like masses and tissue from around the eyes for those with head and neck-limited disease.
IgG4-RD News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Recent Posts
- Neurological symptoms may be more common in IgG4-related disease
- Guest Voice: Living with IgG4-RD is the new hobby I didn’t want
- In the language of illness, words can heal, or they can hurt
- IgG4-RD patients with allergy history are more likely to relapse: Study
- Eye muscle involvement may raise relapse risk in IgG4-related eye disease
