Uplizna (inebilizumab) for IgG4-related disease
Last updated May 16, 2025, by Marisa Wexler, MS

What is Uplizna for IgG4-related disease?
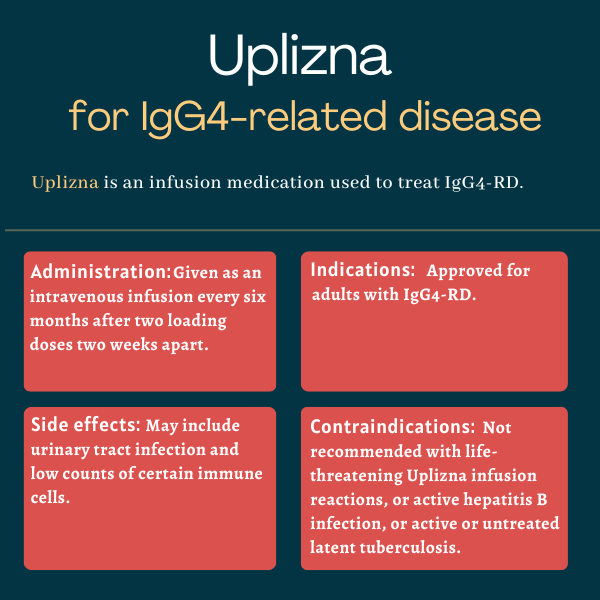
Uplizna (inebilizumab) is an infusion therapy approved in the U.S. for adults with IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD).
Administered via infusions into a vein, or intravenously, the therapy works by killing B-cells, a type of immune cell that, in people with IgG4-RD, forms clumps inside tissues and produces large amounts of IgG4, a type of antibody.
Uplizna blocks a protein called CD19 that is present at the surface of B-cells from their early stages of maturation to their most mature stage, called plasma cells. These are the cells that produce high levels of antibodies.
CD19-positive B-cells are thought to contribute to IgG4-RD and periods of symptom worsening, called flares, by promoting the inflammation and tissue scarring, or fibrosis, that mark the rare disease. IgG4-RD can affect nearly any organ system, and flares can lead to progressive organ damage and failure.
By lowering the levels of CD19-positive B-cells, Uplizna should lower IgG4-RD disease activity and the risk of flares.
The therapy, which was the first to be approved for IgG4-RD, is sold by Amgen.
Therapy snapshot
| Brand name: | Uplizna |
| Chemical name: | Inebilizumab |
| Usage: | Used to treat adults with IgG4-RD |
| Administration: | Intravenous infusion |
Who can take Uplizna?
Uplizna is approved in the U.S. for treating IgG4-RD in adults.
It is not recommended for anyone with:
- a previous life-threatening reaction to the therapy’s infusion
- active hepatitis B, a viral infection that mainly affects the liver
- an active or untreated latent tuberculosis infection, a bacterial infection that usually attacks the lungs.
Also, Uplizna should not be given to patients with any other active infection, and treatment should be delayed until the infection is resolved.
How is Uplizna administered?
Uplizna is administered under the supervision of a healthcare professional as intravenous infusions that last about 90 minutes. The recommended dose is 300 mg, the first two infusions being given two weeks apart, with subsequent infusions administered every six months.
Patients need to be monitored for potential reactions during and for at least one hour after each infusion.
Uplizna in clinical trials
Uplizna’s approval in the U.S. for IgG4-RD was mainly supported by data from a placebo-controlled Phase 3 clinical trial (NCT04540497) that enrolled 135 adults with active IgG4-RD. Results showed that, compared with the placebo, one year of treatment with Uplizna significantly:
- reduced CD20-positive B-cells and IgG4 levels in the blood
- lowered the risk of flares by 87%
- reduced the annualized rate of treated flares by 86%
- increased the likelihood of achieving flare-free, treatment-free complete remission by more than four times
- increased the chances of achieving flare-free, glucocorticoid-free complete remission by nearly five times.
Uplizna treatment was also associated with a tenfold drop in mean doses of glucocorticoids, anti-inflammatory medications that are commonly used in IgG4-RD, but whose long-term use can cause serious side effects. In addition, more than twice as many Uplizna-treated patients were able to completely discontinue glucocorticoid treatment relative to those given the placebo.
Uplizna side effects
Most side effects observed with Uplizna in people with IgG4-RD are mild to moderate in severity. The most common ones include:
- urinary tract infections
- low counts of certain immune cells called lymphocytes (lymphopenia).
Some patients have experienced reactions during or shortly after Uplizna infusions, most commonly the first. Patients should be monitored for signs and symptoms of such reactions, which may include:
- headache
- nausea
- sleepiness
- shortness of breath
- fever
- muscle pain
- rash
- palpitations
- a serious allergic reaction known as anaphylaxis.
Management of infusion reactions may involve pausing or slowing the infusion, or administering additional treatments. If a life-threatening infusion reaction occurs, Uplizna should be permanently discontinued.
Uplizna treatment can increase the risk of infections, as it depletes B-cells, which produce antibodies to help fight off infections. This can lead to low antibody levels and an increased risk of infections, including worsening of hepatitis B or tuberculosis, and a severe brain infection called progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy.
Therefore, the therapy should be delayed in people with an active infection until the infection resolves. To minimize infection risk, patients should receive all recommended vaccinations at least one month before starting Uplizna. Live virus vaccines are not recommended during Uplizna treatment and should be avoided in babies exposed to Uplizna during pregnancy until adequate B-cell levels are confirmed.
Based on animal data suggesting that Uplizna use during pregnancy may cause harm to the developing fetus, patients with the potential to become pregnant are advised to utilize an effective form of contraception while taking Uplizna and for at least six months after stopping treatment.
IgG4-related Disease News is strictly a news and information website about the disease. It does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. This content is not intended to be a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the advice of your physician or other qualified health provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition. Never disregard professional medical advice or delay in seeking it because of something you have read on this website.
Recent Posts
- Neurological symptoms may be more common in IgG4-related disease
- Guest Voice: Living with IgG4-RD is the new hobby I didn’t want
- In the language of illness, words can heal, or they can hurt
- IgG4-RD patients with allergy history are more likely to relapse: Study
- Eye muscle involvement may raise relapse risk in IgG4-related eye disease